We are in the age of Artificial Intelligence that depends on machine vision. This technology surge has necessitated thinking about camera systems in new ways because machine vision systems based on neural networks have different requirements from camera systems intended for human perception.
Norman Koren, Imatest’s founder, has developed a novel approach for evaluating the quality of machine vision systems based on information theory, which is widely used in electronic communications. The image signal and noise (or SNR) are entered into the Shannon-Hartley equation to calculate Information capacity, which is the maximum amount of information that can pass through a channel (i.e., the camera system) without error. Simply put, it is a measure of a camera’s “goodness.” By measuring the signal and noise from the same slanted edge region of an image, greater understanding can be gained for a camera system’s fundamental capabilities and potential performance. Traditional measurements such as SNR and MTF50 by themselves are not indicative of the fundamental image information, and hence they are insufficient to derive machine vision performance metrics such as detection confidence levels.
Megan Borek; Imatest LLC; Boulder, CO, USA
This paper was presented on 2025-02-05 at Electronic Imaging 2025
Abstract:
Accurate representation of diverse skin tones in photography has been a longstanding challenge due to biases toward lighter skin in traditional reference materials used for film and digital photography, such as Kodak’s “Shirley” cards and the Fitzpatrick scale. These and other tools, such as the ColorChecker Classic, have offered limited ranges of skin tones and do not capture the full diversity of human skin, including variations in shades, undertones, and exposure behavior. In this study, we evaluate the application of the 10-point Monk Skin Tone Scale, developed by Harvard’s Dr. Ellis Monk, to camera testing and characterization using printed skin tone charts. The Monk scale is applied to color-matched printed faces for testing cameras with facial detection capabilities. We compare the measured CIELAB values and reflectance spectra of these printed targets to those of other commonly used skin tone references, and to data measured from real human skin. Additionally, we assess the performance of these printed targets in photographed scenes in terms of exposure accuracy and color reproduction. This research identifies limitations and strengths of current printed skin tone scales and charts in representing actual human skin tones, and introduces a novel solution for improving equitable camera calibration and characterization protocols. (more…)
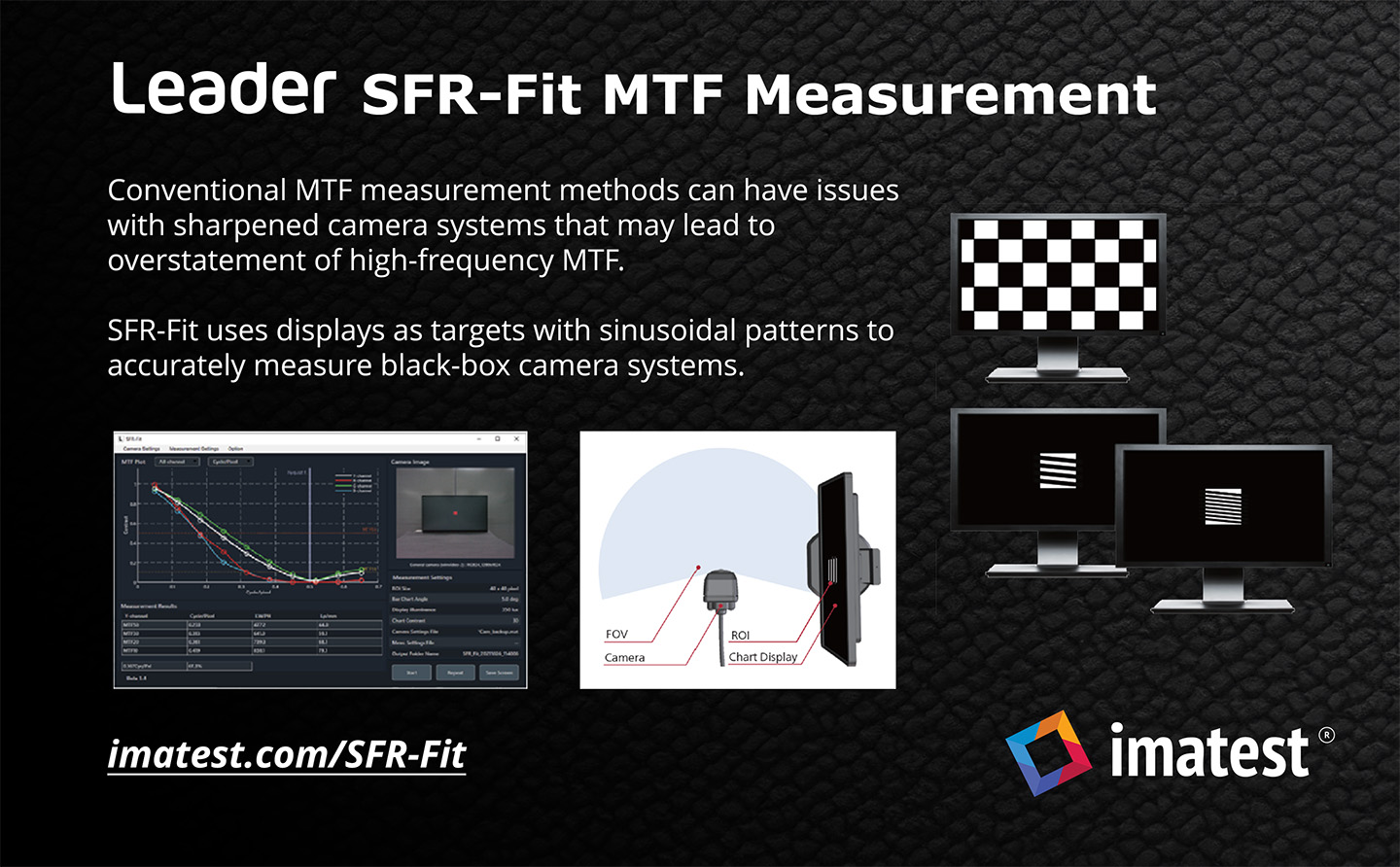
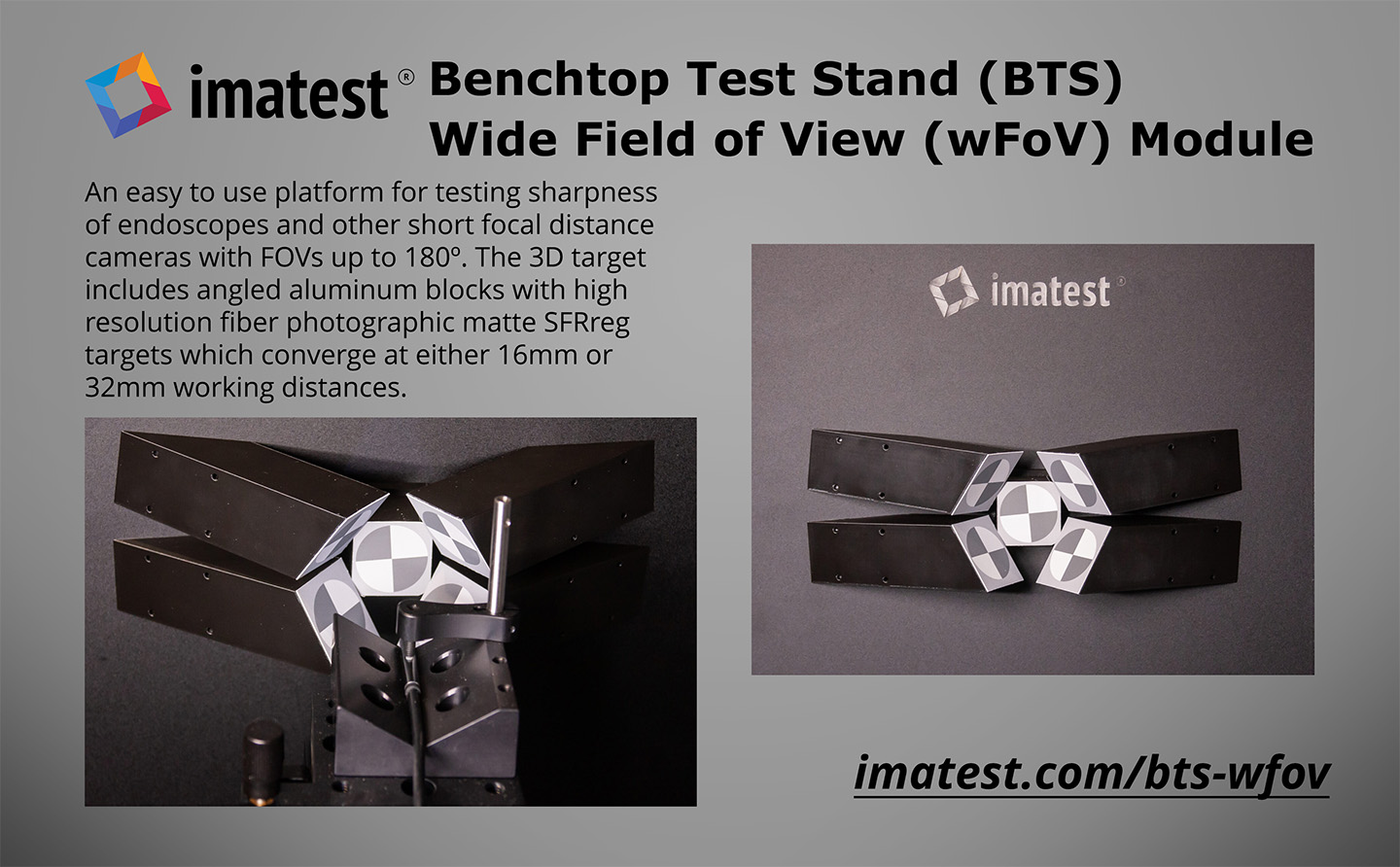
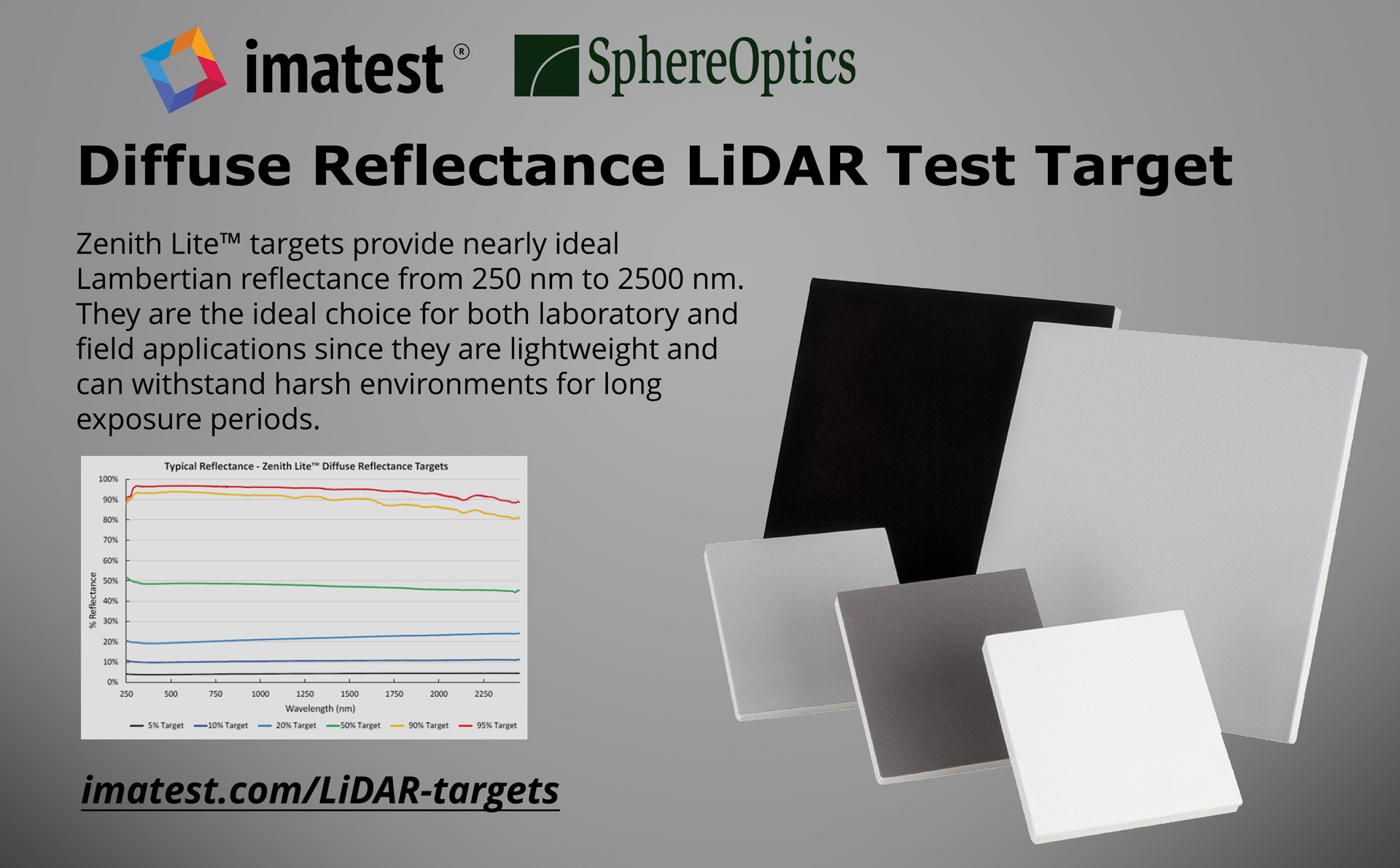
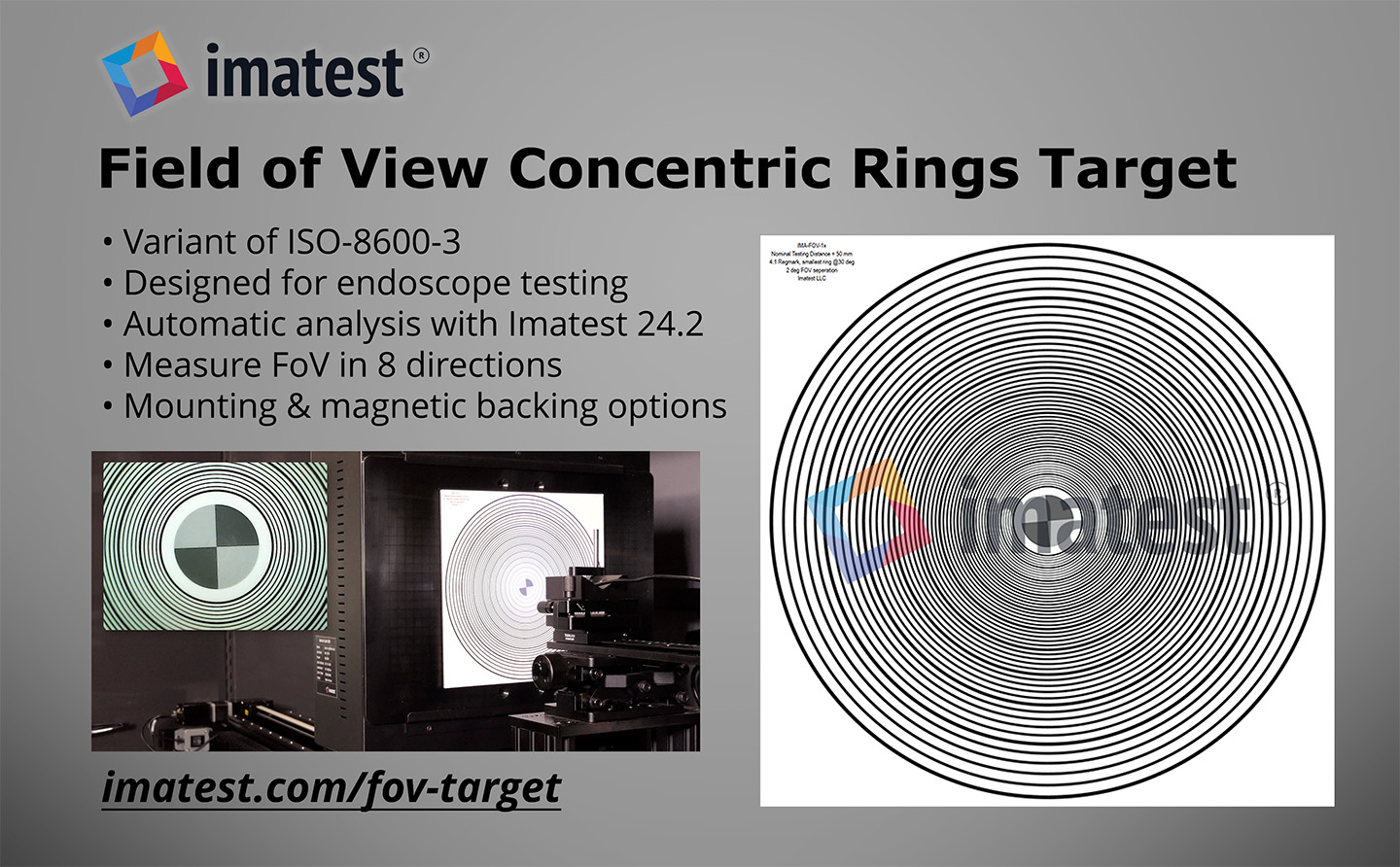
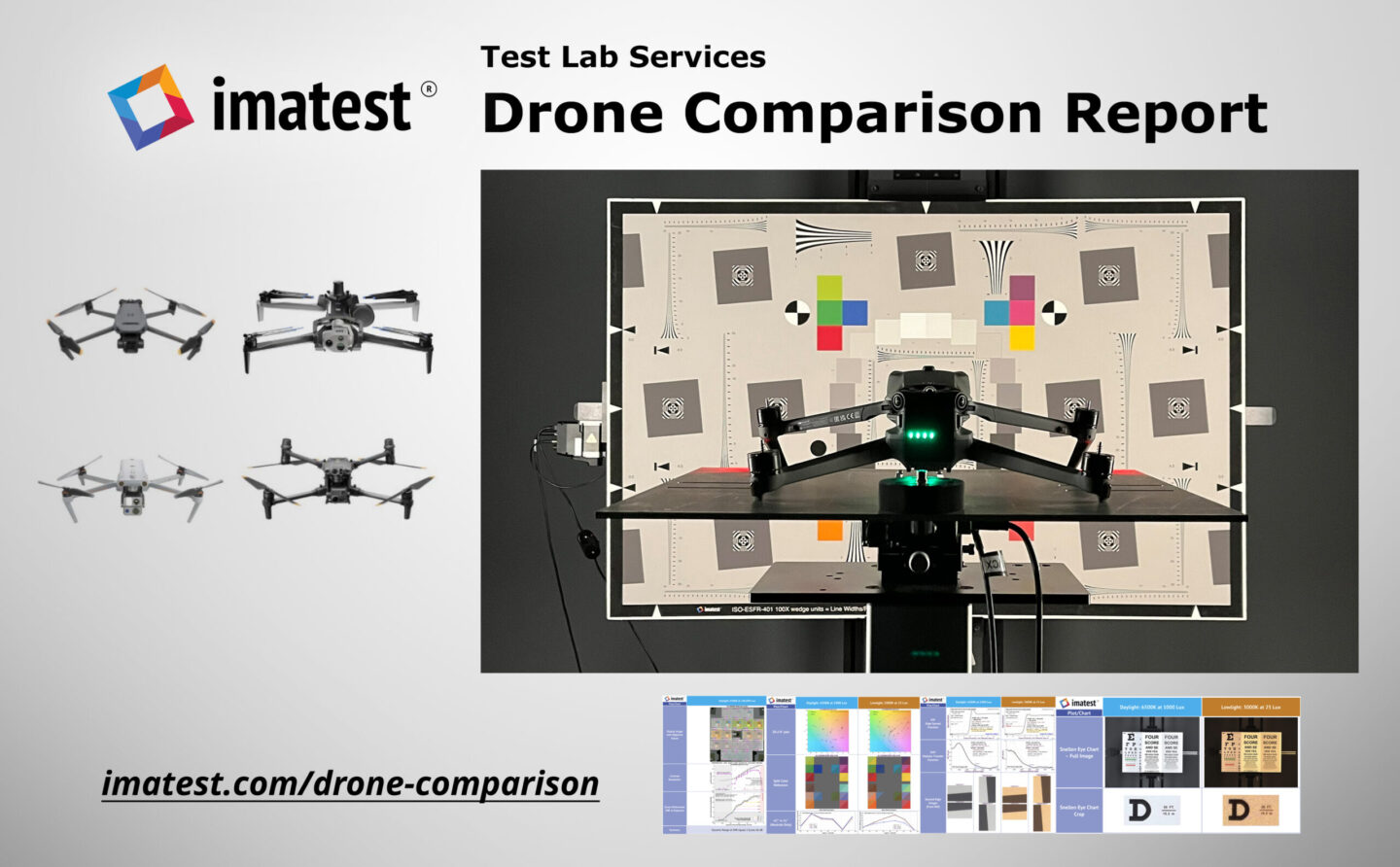
In 2024, Imatest greatly increased our image quality testing capabilities with significant advancements across software, hardware, charts, and solutions. We introduced software updates like versions 24.1 and 24.2, alongside the innovative Leader SFR-Fit. Hardware developments included a fully motorized modular test stand, advanced lighting systems, precision sensors, and magnetic chart holders. New chart designs such as the field-ruggedized target, diffuse reflectance LIDAR target, and diverse skin tone face targets enhanced testing precision. Imatest participated in key conferences like Autosens Europe and Electronic Imaging, showcasing solutions for LiDAR, drones, and test lab services. We released several posts exploring topics including light measurement, and endoscope testing, ensuring a comprehensive view of imaging technology trends.
Software


Hardware

Charts
Conferences / Exhibitions
Solutions
Posts
See Also
Concentric ring FOV, ISO Sharpness target support, batch folder processing, console panel, macOS Sequoia