Search Results for: MTF
Some Imatest calculations up to v5.1 inappropriately averaged zeros with summary metrics
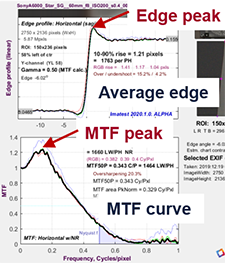
Problem Certain imatest calculations in version 5.1 and below produced zeros when the calculation was not determined. These zero values could be inappropriately averaged with summary metrics which lead to these summary metrics being underreported. The problem includes, but is not limited to the following summary metrics: Chromatic Aberration (CA) summary calculations CA_areaPCT_summary, CA_crossingPCT_summary, CA_R_G_PCT_summary, CA_B_G_PCT_summary where the individual outputs in CA_area_Pct_corner, CA_cross_Pct_corner, CA_crossing_R_G_PCT_corner, CA_crossing_B_G_PCT_corner, CA_crossing_R_G_Pxls, CA_crossing_B_G_Pxls, include zeros. MTF Summary metrics where higher frequency MTF values that are not achieved, and incorrectly reported as zero (corrected in v5.1.28) Solution Take care not to use any summary metrics where the […]
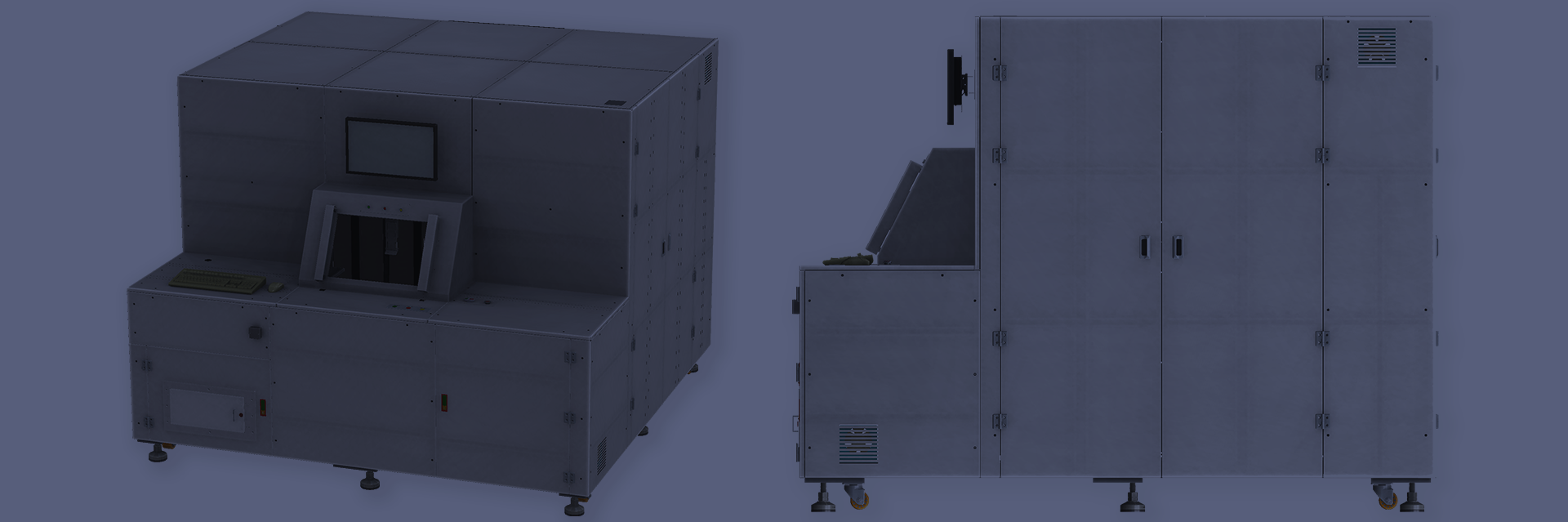
Imatest Manufacturing Equipment
Using the right equipment is essential to manufacturing products successfully. Automated test machines help maximize your workspace, reduce human error, and increase production speed and precision. The right test machines support best manufacturing practices that enable companies to produce high-quality imaging systems. Imatest IT on the Production Line Imatest IT integrates key module functionality with custom testing programs. With this solution, you can quickly test products on the production line to maintain quality standards. At Imatest, we make communicating data across the supply chain easier since tests and results are standardized. Imatest IT can also balance yield with image […]
Imatest Releases Version 2020.1
Imatest, a global image quality testing solution provider, is pleased to announce Imatest 2020.1 that adds new features on top of the major enhancements made in version 5.2. This new release further enhances the software with stability updates and regular improvements. See the Imatest Change Log for details.
Imatest EI Presentations Now Online
The research papers presented at this year’s Electronic Imaging Symposium (EI 2020) by Imatest engineers are now available.